New York
Charter Schools Movement State Timeline
1990's

Widespread concern focuses on the struggles of public schools in New York. Schools in New York City, where graduation rates fell below 50%, were seen to be most in crisis, but schools in many other major cities such as Buffalo were understood to lack a vision for improvement. The New York City Chancellor vowed to take direct control of some high schools experiencing dropout rates approaching 80%
https://timesmachine.nytimes.com/timesmachine/1990/01/05/issue.html
Fall 1992

Long time New York philanthropists, Joe and Carol Reich, after years of struggle to overcome restrictive regulation and bureaucratic restraint, succeed in opening the Beginning with Children School, a public-private hybrid school that received freedoms denied other public schools. The effort generates unprecedented results in a high need community and provides an example that autonomous schools have the potential to greatly improve educational opportunity for tens of thousands of historically underserved students.
https://timesmachine.nytimes.com/timesmachine/1990/12/20/issue.html
January 1998

Inspired by the Beginning With Children example, and of reforms efforts happening in other states, New York Governor George Pataki proposes that the state approve a charter school law in order to catalyze bold reform of the state’s public schools. The proposal draws bi-partisan supporters, including Former U.S. Representative Floyd Flake, members of the Legislature’s Black and Puerto Rican Caucus and Buffalo’s Democrat Mayor Anthony Masiello. But opposition in the Legislature, spurred on by teachers’ unions and the education establishment, leads to the proposal failing to make progress during the regular session.
https://www.c-span.org/video/?98548-1/york-state-state-address
https://www.newspapers.com/image/877079734/
https://www.newspapers.com/image/712868346/
https://www.c-span.org/video/?153136-1/charter-school-movement
December 1998

Seizing upon an opportunity late in the year, New York Governor George Pataki refuses to approve a pay raise for state legislators unless they approve a strong charter school law. The original statute allows for the creation of up to 100 charter schools with half to be approved and overseen by the pro-reform State University of New York Board of Trustees. The other half would be approved by the state Board of Regents, which had opposed the proposal.
https://timesmachine.nytimes.com/timesmachine/1998/12/18/issue.html
September 1999

New York’s first charter school, Sisulu Children's Academy, opens in Harlem. It was co-founded by the Rev. Wyatt Tee Walker, former chief of staff to Martin Luther King Jr., and businessman-philanthropist Steven Klinsky. The school is now named Sisulu-Walker Charter School of Harlem.
https://timesmachine.nytimes.com/timesmachine/1999/09/08/issue.html
https://www.newspapers.com/image/479490906/?terms=sisulu%20charter%20academy
https://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-srv/politics/campaigns/wh2000/stories/pmbush100599.htm
2000

The New York Times reports that a “boomlet” of charter school expansion is underway, with 13 new schools approved by the State University of New York Board of Trustees. The year also sees the founding of the New York Charter Schools Association, the first advocacy and support organization for the state’s charter school sector.
https://timesmachine.nytimes.com/timesmachine/2000/01/26/issue.html
2002

'New York City Mayor Michael Bloomberg appoints Joel Klein as Chancellor of New York City Department of Education. One year later they launch a bold reform program that includes adding high quality charter schools and making vacant district school space available to charters. We decided the space should follow the child too,” Klein said. ”Co-location” makes possible a tremendous growth in charters throughout New York City.
https://www.newspapers.com/image/709150654/
https://charterlibrary.org/library/inside-the-founders-joel-klein/
https://timesmachine.nytimes.com/timesmachine/2002/07/30/issue.html
2001 - 2005

While progress is striking in New York City, charter school growth occurs in several upstate communities as well. KIPP opens schools in both Buffalo and Albany. In Rochester a number of successful charter schools open, including Eugenio Maria de Hostos Charter School, which was founded by long-time Latino education activists. In this period, King Center Charter School also opened in Buffalo, a school that goes on to become among the highest performing public schools in the state.
https://www.newspapers.com/image/136718213/
2004

Harlem Children’s Zone opens its Promise Academy Charter Schools which, as was portrayed in Paul Tough’s influential book, Whatever it Takes, go onto become highly successful, ultimately sending thousands of students to college. The organization and its transformational leader, Geoffrey Canada, are often celebrated by President Barack Obama, ultimately leading to a federally supported replication effort to create 20 similar organizations across the country providing high quality public education at the heart of a comprehensive suite of other support services to students and community members.
https://www.newspapers.com/image/347995134/
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Xh5QRMaa_KE
https://www.amazon.com/Whatever-Takes-Geoffrey-Canadas-America-ebook/dp/B003JTHWDW
2004

The New York City Charter School Center is created in partnership with New York City Mayor Mike Bloomberg and Schools Chancellor Joel Klein. The Center’s mission is to accelerate the growth of high quality charter schools. In short order, the Center becomes a recognized source of support and expertise about all things charter occurring within the city and ultimately helps the city’s sector grow to serve well over 100,000 students.
2005

Research begins to show New York charter schools generating strong academic outcomes relative to traditional public schools. The results draw widespread attention in major publications across the state. In New York City, separate analysis demonstrates that 8th graders in charter schools are significantly outperforming their counterparts in district schools in English Language Arts. Such evidence builds pressure on state policy makers to lift the cap on charter schools.
https://www.newspapers.com/image/877137768/
2006

Eva Moskowitz, one-time New York City Council Education Committee chair and a former teacher, opens Harlem Success Academy. The school’s first open lottery generates local news as applications far exceed spaces available. In 2008, three additional schools open and the schools’ academic results consistently place them among the highest performing public schools in New York. Over the next decade and a half, Success Academy grows to open dozens of schools serving nearly 20,000 students, while engaging parents to become involved in activism supporting charter schools. Along the way the organization becomes one of the most talked about education providers in the country, sparking books and journalism in many national publications.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tAf_XJeKj9Y
https://www.newspapers.com/image/409885200/?terms=eva%20moskowitz%20dummies&match=1
2006 - 2007

In 2006, continued robust growth results in the number of New York charter schools hitting the cap of 100 permitted under state law, leading many state policy makers to call for lifting the cap. Democratic Governor Eliot Spitzer, who had called proposed lifting the cap to 250 in January of 2007, strikes a deal with legislators in March to enact a lifting of the cap from 100 to 200 schools, with 50 specifically set aside for growth in New York City.
https://www.newspapers.com/image/877838257/
2010

In response to Race to the Top federal incentives, the New York Legislature lifts the cap on charter schools from 200 to 460, with 130 additional charters set aside for New York City. The proposal was supported by NYC Chancellor Joel Klein who cited the 35,000 students on charter school waitlists. Ultimately, the bill was championed by Democratic Senators Craig Johnson and Ruben Diaz Sr. who tag-team their floor testimony to highlight that 90% of New York charter school students were low income, with over 70% being African-American or Latino.
https://www.nytimes.com/2010/05/29/nyregion/29charter.html
2014
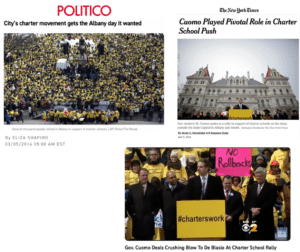
More than 11,000 charter school parents, students and other supporters rally at the state Capitol in Albany during final negotiations over charter school proposals in the state Legislature. The bi-partisan rally helps win passage of a new law requiring the New York City Department of Education to pay rent for new charter schools in the city that are not provided free space in existing district buildings.
2014 - 2018

The continued struggle of urban schools in Upstate New York in combination with early charter schools showing strong promise in communities such as Buffalo and Rochester result in new conversations about how charter schools could become key drivers of citywide education reform. In 2014, the Buffalo School Board formally began consideration of plans to expand public charter schools, and in 2018, a conversation began in Rochester about whether a program of supporting Innovation Schools piloted in Indianapolis could be brought to Upstate.
https://www.newspapers.com/image/878267242
https://www.newspapers.com/image/878240039
2019 - 2022

In 2019, New York City hits the approved limit for the number of charters permitted under state law, effectively creating a moratorium on new charter school growth in the city, as tens of thousands students continue to wait on waiting lists. But despite the cap, charter schools grow steadily during the Covid pandemic while traditional public schools see their enrollment plummet.
https://www.nytimes.com/2022/11/21/nyregion/nyc-charter-schools.html
https://nypost.com/2021/09/22/charter-schools-gained-over-public-during-pandemic-report/
2020

Attention across the state focuses on the New York Board of Regents decision to not renew the charter for Buffalo Science Charter School, one of the highest performing public schools in the state. In the context of its renewal Buff Sci was also seeking authority to open a new school in Buffalo in response to parent demand. Community leader input, parent activism and widespread press condemnation results in the Regents ultimately reversing their decision, allowing Buff Sci to continue operating their existing school and to grow.
2023

Following through on a one-word campaign promise to support the lifting of the charter school cap in New York City, New York Governor Kathy Hochul pushes through a proposal to increase by 14 the number of charter schools permitted to operate in the city. While many lament how few new charters are permitted, the change in law results in near immediate approval of five new schools to open in the fall of 2024, the first schools to open in the city in six years.
https://www.empirecenter.org/publications/hochuls-charter-school-fight-pays-off/
2023

Public charter school leaders, elected officials and community supporters gather in Manhattan to celebrate the 25th anniversary of the passage of the New York State Charter Schools Act of 1998. Hosted by the New York Charter Schools Association, the event features notable guest speakers, including former Governor George Pataki, as well as performances and presentations from public charter school students, past and present. "Today, hundreds and hundreds of thousands of New York kids have had a better education because of you,” said Governor Pataki.

